You will be redirected to a Leads.io registration page.

You need to fill in only 1 form to get free quotes

We call you to confirm your enquiry

Receive quotes from local installers
- GreenMatch.com
- Heat Pumps
Heat Pumps in 2025: What, How & Why? + Pros And Cons
How Does a Heat Pump Work and Why Use Them?

Heat pumps work by pumping or moving heat from one place to another by using a compressor and a circulating structure of liquid or gas refrigerant, through which heat is extracted from outside sources (such as the heat of the soil in the garden or the outdoor air) and transferred to your house.
As a result of this, heat pumps require much less electricity, as opposed to electric boilers, and can often achieve a 300-400% efficiency rate. As the amount of heat energy produced is markedly higher than the energy consumed.
Heat pumps come with multiple advantages for your home. And besides heating your house, during the summers, the cycle can be reversed and the unit acts like an air conditioner.
The International Energy Agency, in their latest special report, stresses that no new gas boilers should be sold after 2025 if Net Zero targets are to be achieved by 2050. With an expected 19 million heat pump installations in new homes by 2050, their role in reducing the US’s carbon emissions at a domestic and national level has drastically increased.
By simply clicking the button below, we’ll provide you with up to 3 free quotes from qualified installers available in your area. This way you don’t have to waste hours of your time researching and you can objectively compare
quotes side by side. What’s more, you’re under absolutely no obligation to accept any of the offers.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
What Are the Pros and Cons of Heat Pumps?

Prior to your decision of purchasing a heat pump system, it is important to inform yourself about heat pumps’ pros and cons. There are a multitude of heat pump advantages, which make them a great investment for the homeowner. But there are simultaneously concerns that have to be regarded.
We will take a look at these advantages and disadvantages in detail below, to help you make an informed decision and make a wise investment in this low-carbon heating technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of heat pumps.
Heat Pump Advantages
Heat pumps can be a fantastic choice for your home in many ways. Listed below are some of the advantages you can get by installing a heat pump.
1. Lower Running Costs
Heat pumps are cheaper to run than systems based on combustion. The more energy efficient the systems are, the greater the long-term savings on energy.
2. Less Maintenance
Heat pumps require less maintenance than combustion heating systems. Certain aspects of the heat pump will need to be checked about once a year, but this can easily be done by yourself. A professional installer will only have to check the heat pump every 3 or 5 years.
3. Better Safety
Heat pumps are safe to operate in general and are also considered to be safer than combustion-based heating systems. This is because they rely on electricity and do not need to burn fuel to generate heat.
4. Reduces Carbon Emissions
A heat pump system reduces your carbon emissions and has an efficient energy-to-heat conversion rate. For example, water source heat pumps can reach impressive efficiency levels of close to 600%.
5. Provides Cooling
When the weather gets warmer, heat pumps are able to reverse their heating process and act like an air-conditioning units. Air-to-air heat pumps can conveniently be switched to a cooling mode during the summer.
6. Long Life Span
The average lifespan of a heat pump is about 15 years, and some can even function efficiently for more than 20 years. They are exceptionally reliable and a steady source of heat.
Heat Pump Disadvantages
Heat pumps are one of the most efficient home heating solutions available. However, there are some drawbacks to consider in when choosing a heat pump.
1. High Upfront Cost
Heat pumps have a large upfront cost, but on the other hand, their operating costs translate to long-term savings on energy bills and lead to a path of reduced carbon emissions.
2. Difficult to Install
Heat pumps are fairly difficult to install considering there needs to be thorough planning and research in order to understand the movement of heat, local geology (specifically for ground source heat pumps), and the heating and cooling requirements for your household.
3. Questionable Sustainability
Some of the used fluids for heat transfer are of questionable sustainability and thus raise environmental concerns. Therefore, it is recommended to use biodegradable fluids.
4. Requires Significant Work
The installation process for a heat pump requires significant work and disruption to your house and garden. A pertinent example would be that penetrations have to be made through the building cladding.
5. Issues in Cold Weather
Air source heat pumps can experience issues such as icing in cold temperatures, which can ultimately damage the system. Although modern heat pumps do often have automatic defrosting.
Their efficiency will also be lower at very cold temperatures, and use more electricity during those cold days. Ground source heat pumps, on the other hand, are much more resistant to cold temperatures.
Always check the Seasonal Performance Factor (SPF) of your heat pump.
6. Not Entirely Carbon Neutral
Heat pumps rely on electricity to operate. Even when not accounting for their production, their carbon footprint will be dependent on how the electricity they use is produced.
With that being said, in comparison to other heating systems, such as an electric boiler, they use much less electricity and extract heat energy from the environment instead.
In either case, if you wish to be carbon neutral, then you should consider renewable energy sources for your home, such as solar.
Are Heat Pumps Worth the Investment?
Heat pumps’ advantages clearly indicate that they represent a smart investment in the long run. Given that you can save on your energy bills (as the mechanism behind the heat pump simply moves heat from one space to another rather than producing it) and that the government can provide you with financial support, heat pumps are absolutely worth it.
The Inflation Reduction Act at the federal level allows you to switch to heat pump systems at a lower cost through tax credits and rebates. There are additional incentives available at the state level that further lowers your overall investment cost. You can also take advantage of the Residential Clean Energy Credit if installing geothermal heat pumps.
Even though the consensus is that heat pumps are a good investment, this doesn’t mean that you should overpay the upfront costs. We can help you ensure that you’re getting the best possible deal on your heat pump installation, as well as save you hours of your time trying to find reliable installers.
Simply click the button below and we’ll provide you with up to 3 free quotes from qualified installers in your area. You’re under no obligation to accept any of the offers, so you don’t need to worry about making a commitment until you’re ready.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
What Are the Different Types of Heat Pumps?
There are various types of heat pumps depending on the source of the heat and the use of that heat in your home. While all types of heat pumps are worth the investment in the US, your choice depends on two things:
Whether you want the heat to be extracted from the soil (which requires digging up your garden for laying pipes underneath), from the ambient air (which requires little space but a fan will constantly emit a low amount of noise), or from a body of water (if you have this available close to your house).
Whether you want the heat to be used for domestic hot water and conventional heating using radiators or underfloor heating, or you prefer heating the home by ventilating with heated air (similarly to how an air conditioner would cool the room).
When the heat source is the soil, we talk about ground source heat pumps. Similarly, the ones using the ambient air or a body of water are called air source and water source heat pumps, respectively. These umbrella terms can then be broken down based on the application. On top of that, other aspects like the heat pump supplier, the size of your garden, and your budget also influence what type of system is the most suitable for your profile: air source, ground source, or water source.
Water Source Heat Pump
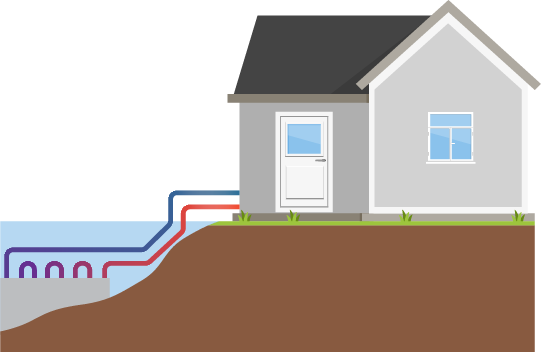
Ground source or geothermal heat pumps are, in most cases, used for heating water. With the help of additional system elements, it is possible to use heated air ventilation with geothermal systems, but it is far more common to use it for conventional radiators and underfloor heating.
Both air source and water source heat pumps can be used for heating water as well as indoor air in your home.
When used for heating water, we refer to air-to-water heat pumps and water-to-water heat pumps. Water source and air-heating systems are called liquid-to-air heat pumps which are a type of specialty product.
Hot air ventilation is usually provided by air-to-air heat pumps. The latter can also be reversed and used for cooling your home without any additional equipment.
Interested in heat pump installation? The best way to find the heat pump system that suits your home’s unique specifications is to consult a professional heating engineer who can assess your needs and then offer quotes for their services.
However, finding installers who you can trust and who will offer fair and accurate quotes, can take considerable time and effort. To truly locate the best deals for new heat pump installations you will need to spend hours calling multiple installers, ensuring they’re properly certified, explaining your heating situation, and asking for quotes.
At GreenMatch, we can save you this extra time and money by directly connecting you with licensed installers from our network, all of them vetted by us. All you have to do is spend a few minutes filling in our quick and easy form and within 48 hours, you’ll hear from up to 3 local heat pump installers.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
What Is a Ground Source Heat Pump?
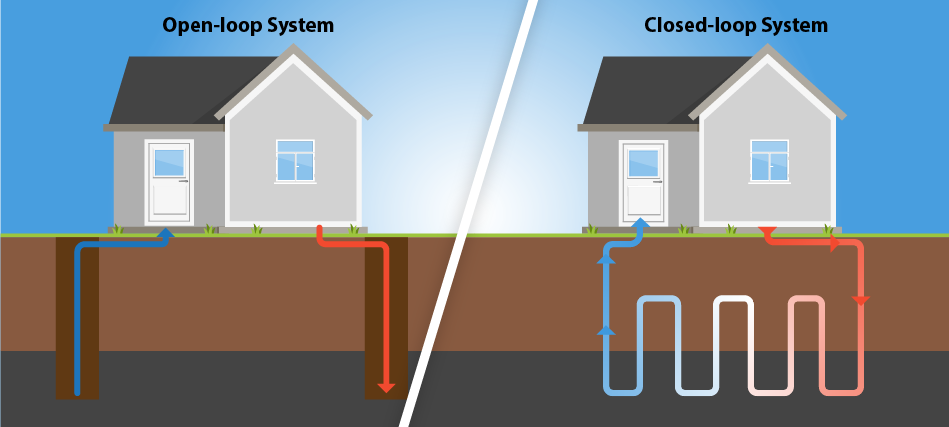
There are a variety of ground source heat pump systems (GSHP). GSHPs can be sub-categorised into vertical and horizontal systems and open- and closed-loop systems. The different choices affect the prices of ground source heat pumps.
Ground Source Heat Pumps - How do they work?
Open-Loop Systems
Despite being called a ground source heat pump, open-loop systems pump up groundwater from deep underneath the soil, then after extracting the heat from it, the water is pumped back. Such a system has higher running costs, as you need to make sure the water is unaffected and need to comply with regulations for using such natural water sources.
Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop systems circulate an antifreeze liquid through a closed plastic polymer tubing that is buried in the soil.
Vertical ground source heat pump systems: Such a system requires a hole to be drilled into the ground, normally at a depth of 50–150 metres. At greater depths, the temperature increases, warming the anti-freeze liquid. This liquid then comes back through an exit hole, where it then heats up the refrigerant that stays in the house within a second system. The system’s main disadvantage is its high initial investment.
Horizontal ground source heat pump systems: This type of GSHP is less costly than a vertical system, as it is less
complex. To install a horizontal geothermal system, the ground has to be dug out just below the frost line. Then, coiled pipes are laid down into the ground, creating spirals. A liquid is sent through the system which heats up the refrigerant in the second pipe system. Although more affordable, this system requires more garden space and is affected by seasonal changes due to the lower depths of the system’s installation.
Pond/lake source heat pump systems: This type of GSHP is the least expensive of the three closed-loop systems. This system is adapted if there’s an adequate source of water body on site. To install a pond/lake heat pump system, a supply line is run from under the residence to the water body. The supply line pipe is coiled in circles at least 8 ft. under the surface, which prevents freezing of the pipe. However, the water source should meet the minimum requirements of volume, depth, and quality.
What Is an Air Source Heat Pump?
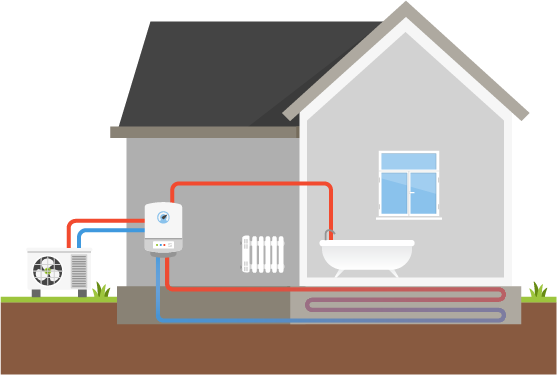
Air source heat pumps (ASHP) use the principles of vapour compression to generate heat. It’s a popular low-carbon heating system, and there are many benefits to using air source heat pumps.
They use outdoor air to heat your home. ASHPs consist of 4 major elements that allow the refrigerant to pass from the liquid form to gas: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator.
Air Source Heat Pumps – How Do They Work?
When the refrigerant passes through the system, it absorbs the heat from the outside air. Then, the compressor increases the heat by increasing the pressure. In the condenser, this higher temperature heat is transferred to the heating and hot water circuits of your home.
After that, the medium-temperature liquid flows into the expansion valve whereupon the release of pressure, its temperature also drops. Finally, the now cooled down liquid is returned to absorb more heat from the air and repeat the process.
ASHPs can be used for heating water for domestic use, radiators, and underfloor heating. Such systems are called air-to-water heat pumps (A2W). If suddenly a large amount of hot water is needed, they are also equipped with an electrical resistance heating element that would supply additional heated water (at a lower efficiency rate, though).
Alternatively, air source systems can be used for heating and cooling the indoor air using air-to-air heat pumps (A2A). These work similarly to an air conditioning unit but can both heat and cool the house efficiently, adding to the list of benefits of air-to-air systems.
Factors to Consider – to See if Heat Pump is the Right Solution for You
Warranty Periods of Heat Pumps
Most manufacturers offer a 5-year warranty on heat pump systems but the warranty can be extended if you
register the product. Upon registering the product, you get an extended 5-year warranty, a total of 10 years. All you are required to do is fill out a form and register the product. There may be differences in labor warranties from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Maintenance of Heat Pumps
A heat pump’s lifespan is approximately 15 years or more. With proper maintenance, their life can be extended to up to 50 years.
They do require regular maintenance: yearly checks are recommended, and a professional installer needs to pay the system a look every 3 to 5 years. In the wintertime, you may also need to defrost the heat pump manually.
After the check-up, the installer should leave written details of the system’s condition and any indications for possible future issues.
In general, maintenance requirements are quite low, as there is no need for crucial safety checks. The usual parts to inspect before starting the system are the pump itself, the external pipes, as well as the electronics and parts of the fittings.
Find the Best Suppliers of Heat Pumps in the US
Heat pumps, whether ground source, air source, or water source, represent excellent opportunities for upgrading your home, as they not only provide you with a solid return on investment but also improve the quality and value of your home.
Finding fair and accurate installation quotes takes careful planning and research. You could risk overpaying for supply and installation from a company that operates nationwide. Why not let GreenMatch take the hassle out of sourcing quotes and directly connect you with up to 3 licensed installers instead?
Simply fill in our quick easy form, and our team will find the best installers for your home’s unique specifications. In 48 hours, you will hear from up to 3 locally based installers, saving time from searching for and researching installers yourself.
Comparing multiple local quotes guarantees the best deal since local installers will likely charge less for the supply and delivery, amounting to less overall installation costs. What’s more, with multiple quotes, you can objectively compare them to locate and lock in the best deal.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
Frequently Asked Questions
The main downside of heat pumps is their initial upfront costs for supply and installation. Installation of heat pumps is also complicated and requires an adequate amount of research and planning. Clogged air filters, and freezing temperatures during winter, only add to the downside of using heat pumps.
The average cost of installing a heat pump ranges between $2,500 to $10,000. However, the cost may go as high as $30,000 if your home requires ductwork or if you’re planning on installing a geothermal heat pump.
Heat pumps are worth the investment as they are highly efficient and can produce 3-4 times more heat with kWh of electricity than they use. This means you’ll enjoy comfortable, warm temperatures for less monthly running costs. Moreover, tax credits and rebates, at both the federal and state level, make it only more worthy of investment.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

